What do Photoelectric Sensors Detect?
Table of Contents
The Basics of Photoelectric Sensors
At their core, photoelectric sensors consist of a light emitter and a receiver. The emitter projects a light beam, often infrared or visible light, towards a target. When an object interrupts or reflects this light beam, the receiver detects the change and sends a signal. This simple principle allows these sensors to perform a variety of detection tasks.
Types of Detection Methods
There are three primary detection methods used by photoelectric sensors:
- Through-Beam Sensors: These sensors have the emitter and receiver placed opposite each other. An object passing between them blocks the light beam, triggering a detection signal. This method offers the longest range and highest reliability in dirty environments.
- Retro-Reflective Sensors: In this setup, the emitter and receiver are housed together, and a reflector is placed opposite them. The light beam travels to the reflector and back to the receiver. When an object interrupts the beam, the sensor detects it. This method eliminates the need to align separate emitter and receiver units.
- Diffuse Sensors: Here, the emitter and receiver are together, but there’s no reflector. The sensor relies on the target object reflecting the light back to the receiver. This method is sensitive to the color and texture of the object, making it suitable for detecting light or reflective materials.
Applications of Photoelectric Sensors
Photoelectric sensors are incredibly versatile. Here’s what they commonly detect:
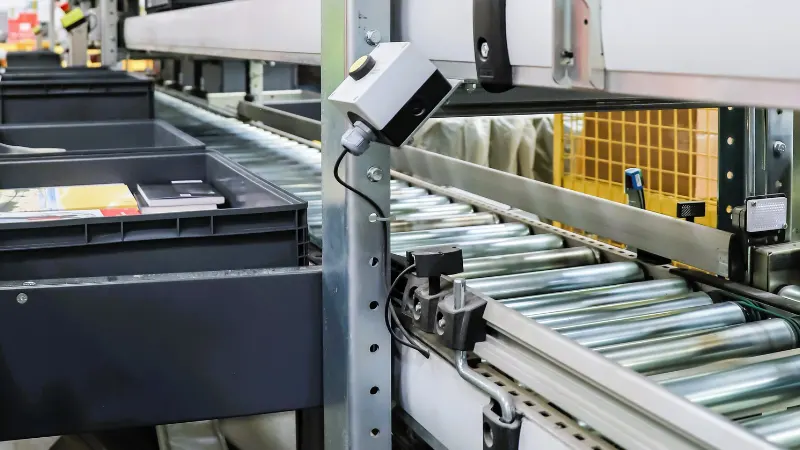
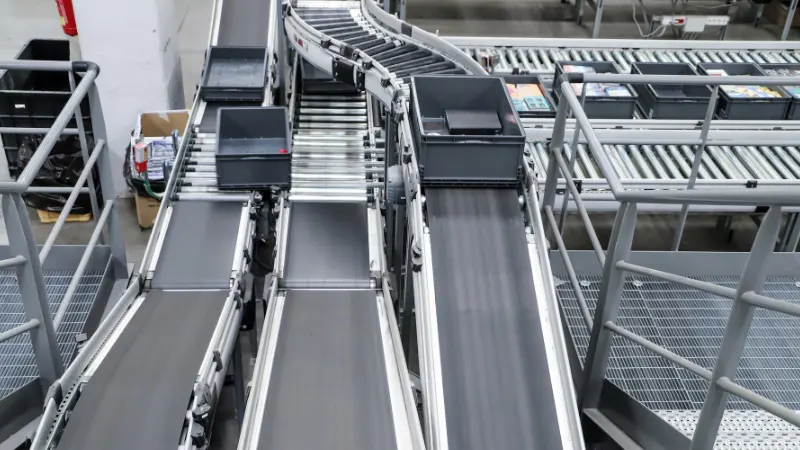
- Object Presence: Detecting if an object is present or absent on a conveyor belt.
- Distance Measurement: Measuring how far an object is from the sensor, crucial in positioning tasks.
- Object Counting: Keeping track of items passing through a production line.
- Color Detection: Identifying objects based on color differences.
- Transparency Detection: Sensing transparent objects like glass or plastic bottles.
Advantages in Industrial Automation
In my experience, integrating photoelectric sensors into automation processes brings several benefits:
- Non-Contact Detection: Since they use light, there’s no physical contact with objects. This reduces wear and tear and is ideal for delicate items.
- Long Detection Range: Especially with through-beam sensors, they can detect objects over considerable distances.
- Fast Response Time: They can detect objects at high speeds, essential for quick-moving production lines.
- Versatility: Suitable for various materials, sizes, and colors.
Challenges and Considerations
While photoelectric sensors are advantageous, there are factors to consider:
- Environmental Conditions: Dust, mist, or smoke can interfere with the light beam. Choosing the right sensor type helps mitigate this.
- Target Material: Highly reflective or transparent objects might require specialized sensors.
- Alignment: Through-beam sensors need precise alignment between the emitter and receiver.
Choosing the Right Sensor
Selecting the appropriate photoelectric sensor depends on the application’s specifics. Here’s what I usually consider:
- Detection Range: How far does the sensor need to detect?
- Object Characteristics: What’s the size, color, and material of the object?
- Environmental Factors: Will the sensor be exposed to harsh conditions?
- Speed of Operation: How fast is the production line moving?
Why Photoelectric Sensors Matter
In today’s automated world, the role of photoelectric sensors cannot be overstated. They enhance efficiency, accuracy, and safety across various industries, including manufacturing, packaging, and logistics.
For example, in a packaging line, photoelectric sensors ensure that each product is correctly placed and packaged. Any discrepancy triggers an alert, allowing for immediate correction. This not only maintains product quality but also reduces waste.
Future of Photoelectric Sensors
Advancements in technology are continually improving sensor capabilities. Features like background suppression, where the sensor ignores objects beyond a certain point, and IO-Link communication for smart sensor integration, are becoming more prevalent.
At Kwoco, we stay abreast of these developments to provide our clients with the latest solutions. Our goal is to support businesses in optimizing their operations through advanced automation products.
Power your projects with brand-new, original Omron, Keyence, Schneider Sensors – in stock, ready now!
Conclusion
Photoelectric sensors might seem like small components in the grand scheme of industrial automation, but their impact is significant. They ensure processes run smoothly, products meet quality standards, and operations are safe and efficient.
If you’re considering integrating photoelectric sensors into your systems or need assistance selecting the right type, don’t hesitate to reach out. With our extensive stock and expert support, we’re equipped to meet your needs promptly.
Feel free to contact me at [email protected] or visit our website at www.kwoco-plc.com for more information.
Contact Us
Just fill out your name, email address, and a brief description of your inquiry in this form. We will contact you within 24 hours.
You May Also Find These Topics Interesting

Decoding the Difference Between Servo Motor and Spindle Motor in CNC Applications
This article dives into the distinctions between servo motors and spindle motors, two critical components in the world of CNC machinery. Understanding these differences is crucial for anyone involved in industrial automation, from seasoned engineers to those new to the field. We’ll explore their unique characteristics, applications, and how they contribute to the precision and efficiency of CNC machines.

What is DCS? A Guide to Distributed Control Systems
Distributed Control Systems (DCS) have revolutionized the way industries manage and control complex processes. This comprehensive guide will delve into the architecture, benefits, and applications of DCS, explaining why understanding this technology is essential for modern industrial automation and control.

France Omron PLC Supplier Near You
In the field of industrial automation, integrity and effectiveness are the foundations of success. As the core of complex systems, the PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) from Omron is definitely a benchmark brand name in the industry.