What is PLC Programming? An Introductory Tutorial on PLC Programming
Table of Contents
This write-up will give a comprehensive description of PLC programming, its features, working concepts, and applications, aiding customers obtain a much deeper understanding of the benefits of PLC programming and make educated choices when selecting suitable PLC products.
What is PLC Programming?
PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) is an industrial control system based upon microprocessor technology, particularly made for automation control.
It executes programmed instructions to regulate production tools, equipment, assembly line, etc, for automated operations. PLC programming describes the process of writing instructions to control the PLC to do certain tasks.
Compared with traditional relay control systems, PLCs provide greater dependability, versatility, and scalability, making them a crucial component of contemporary commercial automation.

7 Key Features of PLC Programming
1. Easy and Easy-to-Learn Programs
The most frequently utilized programming language for PLCs is Ladder Diagram (LD), which has signs and expressions similar to relay circuit diagrams.
For electrical engineers, the Ladder Layout programming language is instinctive and understandable. With a short knowing contour, users can swiftly grasp the language and start programming.
2. Comprehensive Equipment Support and Solid Flexibility
PLC items are extremely standardized, modular, and include a variety of hardware parts for users to select from.
Customers can flexibly set up systems to fulfill different production demands. The setup and wiring of PLCs are also simple and hassle-free, enabling the system to conveniently adjust to various process needs.
3. Powerful Functions and High Performance-to-Cost Proportion
PLC systems supply powerful control features and are very affordable. A small-sized PLC can have hundreds and even countless programmable components and can dealing with complicated control jobs.
PLCs can additionally support communication with other gadgets, allowing dispersed control and centralized administration.
4. Lowered Layout, Setup, and Debugging Workload
By changing standard relay control systems with PLCs, the variety of intermediate relays, timers, counters, and other parts is significantly reduced.
This streamlines control system design, circuitry, and installation work. PLC programs are structured and understandable, which dramatically reduces the design and debugging time.
5. High Dependability and Strong Anti-Interference Capability
PLCs are recognized for their high anti-interference ability, allowing them to operate stably also in high-interference environments.
As a result of the combination of durable hardware and software actions, PLCs have an extremely low failing rate and are identified as one of the most reputable industrial control gadgets.
6. Compact Dimension and Low Power Consumption
Contrasted to standard relay control systems, PLCs have a smaller sized dimension and lower power intake. Using PLCs decreases the setup space required, while the reduced circuitry requirements save a great deal of time and expenses.
In addition, smaller sized control cupboards and lower power consumption make PLCs an extra sustainable choice.
7. Easy Upkeep and Quick Mistake Resolution
PLCs have actually advanced self-diagnostic functions, making it simple to determine faults. If a PLC or an exterior input gadget fails, users can swiftly situate the issue by utilizing the LED signs or the programs device’s feedback. Damaged modules can be changed promptly, decreasing downtime and maintenance costs.
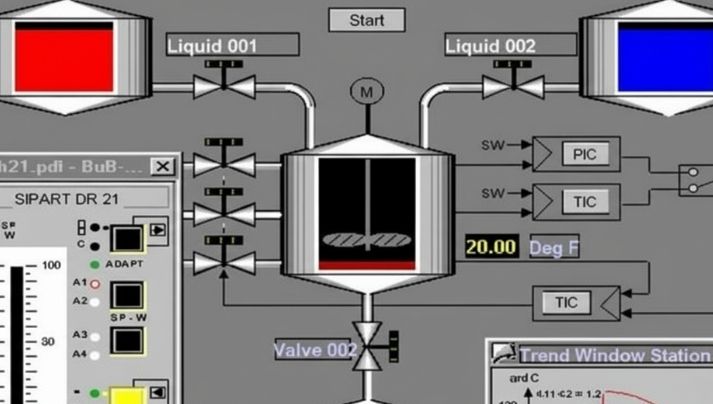
Working Principle of PLC Programming
PLCs operate based on a “sequential scan and continuous loop” mechanism. Throughout procedure, the CPU of the PLC periodically checks and implements the user program saved in the memory, adhering to the series of guideline addresses.
If no dive guidelines exist, it begins with the first guideline and performs every one in sequence until the end, after that returns to the beginning for the following check cycle. Throughout each scan, PLC likewise samples input signals and freshens result statuses.
PLC’s functioning cycle includes three main stages:.
- Input Sampling: The PLC scans all input terminals and stores their conditions in corresponding input status registers.
- Program Execution: The PLC carries out the instructions in the individual program sequentially, processing the information and keeping the cause the output standing registers.
- Output Refresh: After performing the guidelines, the PLC writes the result conditions to the result registers, driving the matching devices.
5 Requirement Programming Languages for PLC
PLC programming includes several languages, each suited for different control tasks. The most common programming languages are Ladder Diagram (LD), Instruction List (IL), Function Block Diagram (FBD), Sequential Function Chart (SFC), and Structured Text (ST).
Users can choose the most appropriate programming language based on their specific control requirements.
1. Ladder Diagram Language (LD)
Ladder Layout is the most generally made use of programs language for PLCs. It utilizes graphical symbols to represent control reasoning, which is really intuitive and familiar to electrical designers.
It is highly visual and easy to understand, making it the recommended option for the majority of control systems.
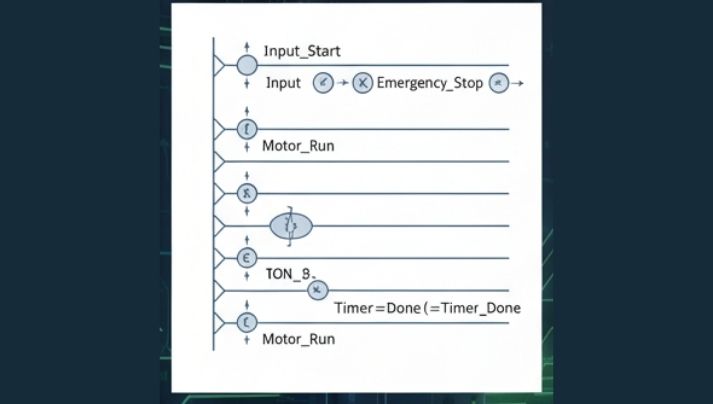
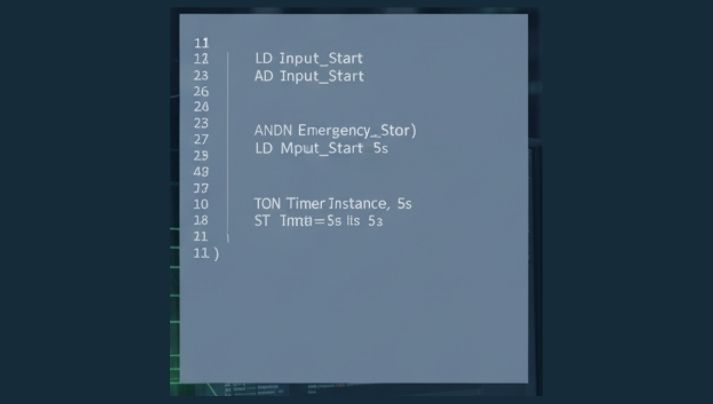
2. Instruction List Language (IL)
Instruction List is a mnemonic programming language similar to setting up language. It consists of procedure codes and operand selections. This language is suitable for hand-held developers, where customers can conveniently set without a computer.
It is compatible with Ladder Representation in PLC programs software application.
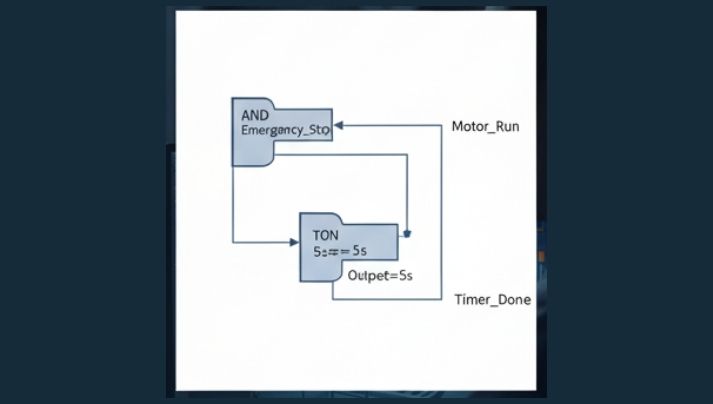
3. Function Block Diagram Language (FBD)
Function Block Representation is utilized for complex systems with modular functions. It stands for control logic in terms of function blocks, making it intuitive and simple to utilize, especially for engineers with a history in digital reasoning circuits.
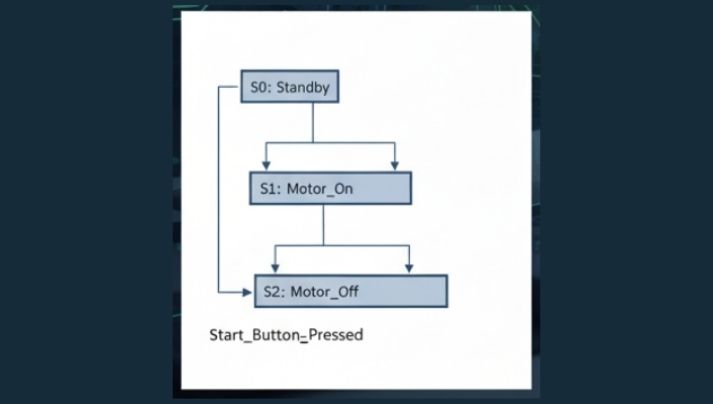
4. Sequential Function Chart Language (SFC)
Sequential Function Graph is designed for consecutive reasoning control. It splits the procedure into steps and transition problems, allowing users to plainly specify each control activity and its order.
This language is particularly helpful for huge systems with intricate control logic.
5. Structured Text Language (ST)
Structured Text is similar to top-level programming languages and is used for complicated control systems. It makes use of text-based summaries to define the connections between numerous variables, making it possible for even more comprehensive control over the system.
It is typically used in bigger PLC systems where other languages are much less ideal.
PLC Programming Newbie’s Guide
1. Flowchart Creation
Flowcharts are symbolic depictions of directions, developing the structure of PLC programming. Customers need to understand logic procedures such as AND, OR, NOT, etc, and their equivalent signs to create the fundamental control reasoning.
2. Creating Ladder Logic Programs
Ladder Reasoning is the heart of PLC programs. It utilizes graphical representations of reasoning to describe control systems. With various signs and guidelines, customers can make complex control systems.
3. Making Use Of Mnemonics for Programs
Mnemonics are symbolic depictions of control instructions, similar to procedure codes. They are used for hand-held programming gadgets and offer a quick and efficient means to compose and debug PLC programs.
Applications of PLC Programming
PLC programming has a large range of applications, including automatic assembly line, equipment, commercial robots, and building automation systems.
PLCs boost production performance, lower labor costs, and can operating in extreme settings. Therefore, PLC programs has become a crucial part of modern commercial automation.
Conclusion
PLC programming, as the core modern technology of industrial automation control, provides high efficiency, adaptability, and reliability. It has actually ended up being a vital component of numerous production lines and automation systems.
By finding out PLC programs, users can enhance the performance of their control systems, maximize manufacturing procedures, and reduce system downtime. When selecting PLC products, individuals need to choose the ideal programs language and controller design based on their certain needs to achieve much more effective computerized production.
If you are looking for PLC programs services or automation devices, feel free to get in touch with Kwoco. We offer world-leading Omron and Mitsubishi PLC products and can offer customized solutions based upon your details needs.
Contact Us
Just fill out your name, email address, and a brief description of your inquiry in this form. We will contact you within 24 hours.
Product Category
Hot Sale Products
You May Also Find These Topics Interesting

Demystifying the Air Circuit Breaker: Your Comprehensive Guide
This article delves into the fascinating world of air circuit breakers (ACBs), explaining their function, types, working principles, and applications. Whether you’re a seasoned professional in the industrial automation sector or simply curious about the technology that powers our modern world, this comprehensive guide will provide you with all the essential knowledge you need about ACBs, making it a worthwhile read for anyone interested in understanding these critical components of electrical systems.

A Deep Dive into Kwoco’s Successful Cooperation with Japanese Public Companies
A Deep Dive into Kwoco’s Successful Cooperation with Japanese Public Companies Have you ever questioned whether a new supplier can

What Are the Characteristics of the Five Major PLC Programming Languages?
What Are the Characteristics of the Five Major PLC Programming Languages? In the world of industrial automation, choosing the right







