Choosing the Right Terminal Block: A Complete Guide
Understanding the key types, electrical and mechanical considerations, safety ratings, and additional design factors is essential to making the right choice. This guide explores everything you need to know to select the ideal terminal block for your needs.
Table of Contents
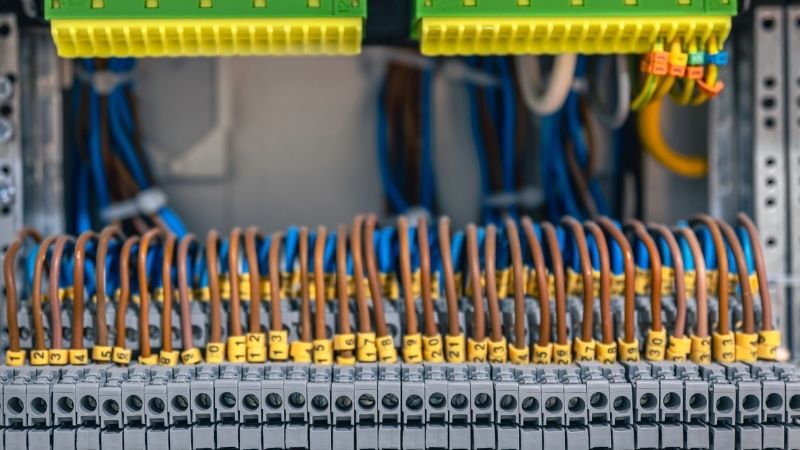
What is a Terminal Block?
A terminal block is a modular, insulated housing designed to connect multiple wires securely, often used in industrial and electrical systems where reliable and well-organized connections are essential. These blocks include clamping components that hold the wires in place, often providing a simple means to swap connections during inspection or maintenance.
Commonly known as connection terminals, screw terminals, or simply connectors, terminal blocks are a staple in creating safe, effective wire management solutions in complex systems.
Types of Terminal Blocks
Terminal blocks come in a variety of styles, each suited to different applications. Here’s a breakdown of some of the most common types:
PCB Mount Terminal Blocks: Known as wire-to-board terminal blocks, these mount directly onto a PCB (printed circuit board). They secure the wires through a clamp mechanism and are often used in electronics and smaller devices.
Barrier Strips: These use a screw-down method to hold ring or spade terminals, providing secure connections that can withstand vibration. Barrier strips are ideal in applications where reliability under movement or jarring conditions is essential.
DIN Rail Terminal Blocks: Mounted on standardized DIN rails, these versatile blocks are suitable for wire-to-wire or ground connections. They are widely used in industrial control panels and automation systems due to their ease of installation and modular configuration.
Each type offers unique features, and selecting the right one depends on your system’s requirements and installation environment.
Key Electrical Considerations for Terminal Blocks
When selecting a terminal block, it’s crucial to evaluate the electrical parameters to ensure compatibility with your system:
Current Rating: This defines the maximum current the block can handle without overheating. Always choose a block with a rating at least 1.5 times the maximum expected current in your system to prevent overheating and potential failures.
Voltage Rating: The maximum voltage a terminal block can safely manage depends on the material and pitch of the block. Ensure the block’s rating exceeds your system voltage to prevent insulation breakdown or other issues.
Wire Size: Confirm that the terminal block supports the range of wire sizes used in your application, from stranded to solid core wires, as different blocks are compatible with specific wire gauges.
Electrical considerations are paramount to ensure the block can withstand the demands of your application without compromising safety.
Key Mechanical Considerations for Terminal Blocks
The physical design of the terminal block also plays a critical role in its suitability for various installations. Here are some important mechanical aspects:
Wire-Entry Orientation: Terminal blocks are typically available with horizontal, vertical, or 45-degree orientations, providing flexibility based on installation space and layout constraints.
Wire-Securing Method: The primary securing methods include screw terminals, push-in clamps, and spring clamps. Each type offers a unique balance of strength, ease of use, and compatibility with wire types.
Module Type: Some blocks are interlocking, allowing for customized configurations by snapping multiple modules together, while others are single-piece, providing a fixed number of poles.
Mechanical design considerations help ensure the terminal block integrates seamlessly into your system while allowing for easy access, installation, and maintenance.
Safety Ratings and Certifications
Safety is a top priority, especially in high-voltage or high-current systems. Terminal blocks are often certified to UL (Underwriters Laboratories) or IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) standards, with many blocks made from materials that meet the UL94V-0 flammability rating. When selecting a terminal block, verify that it complies with the safety certifications required by your project, as these ensure the block can handle potential hazards.
Having certified terminal blocks not only improves the safety of your installation but also ensures compliance with industry standards.
Additional Design Considerations
Beyond electrical and mechanical factors, certain design choices can enhance the usability and effectiveness of your terminal block:
Color Coding and Marking: Colored housings or labeled blocks simplify installation and maintenance, especially in systems with multiple circuits and connections.
Temperature Tolerance: Some applications require terminal blocks to withstand extreme temperatures. High-temperature-rated blocks ensure reliability in such environments.
These additional design elements can streamline assembly and enhance long-term maintenance, helping you create a well-organized, robust system.
Power your projects with brand-new, original Omron, Mitsubishi, Schneider terminals– in stock, ready now!
Conclusion
Selecting the right terminal block is essential for safe and efficient wire management. By understanding the different types of terminal blocks, assessing key electrical and mechanical considerations, confirming compliance with safety standards, and factoring in design enhancements, you can make an informed choice. A well-chosen terminal block will not only meet your current needs but also contribute to a reliable and maintainable electrical system over time.
If you’re seeking a reliable industrial terminal block supplier, contact Kwoco. We supply brand-new, original terminals from top brands like Omron and Schneider, with global shipping available to meet your needs.
Contact Us
Just fill out your name, email address, and a brief description of your inquiry in this form. We will contact you within 24 hours.
You May Also Find These Topics Interesting

Omron PLC Selection Guide for Project Managers
Omron PLC Selection Guide for Project Managers Every project manager faces the challenge of selecting the right PLC (Programmable Logic

Recommended Omron PLC Suppliers in the UK: How to Find a Reliable Partner
In the ongoing electronic makeover of UK production, Omron PLCs have actually long been the favored selection for many automation engineers and procurement managers. Whether in food packaging, automotive manufacturing, or power control systems, Omron PLCs are trusted for their security, high performance, and exceptional compatibility.

10 Essential Insights About OMRON PLC CJ2 Series
10 Essential Insights About OMRON PLC CJ2 Series KWOCO focuses in internationally renowned industrial automation products, I’ve had extensive hands-on